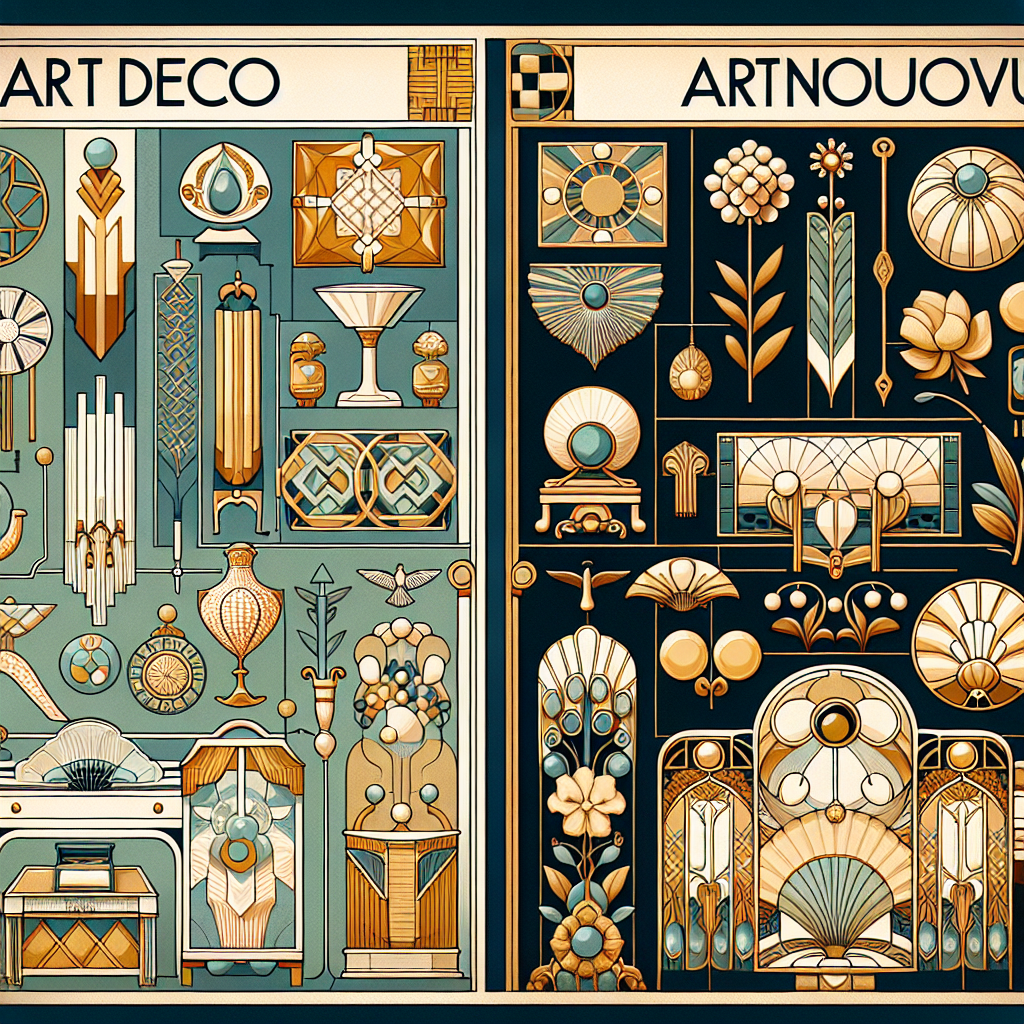
Art Deco and Art Nouveau are two prominent styles that emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Despite both being known for their intricate designs and emphasis on craftsmanship, they differ significantly in their aesthetics, influences, and impact on the world of art and design. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between Art Deco and Art Nouveau, exploring their unique characteristics and the lasting influence they have had on the world of design.
Art Nouveau: A Celebration of Nature and Whiplash Curves
Art Nouveau, which emerged in the late 19th century, is characterized by its organic forms, intricate motifs, and flowing, curvilinear shapes. The style was heavily influenced by the natural world, with designs often incorporating elements such as flowers, leaves, and vines. One of the most distinctive features of Art Nouveau is the use of "whiplash" curves, which are sinuous, flowing lines that create a sense of movement and grace.
The origins of Art Nouveau can be traced back to the Arts and Crafts movement in Britain, which emphasized the importance of handmade craftsmanship and the use of natural materials. However, Art Nouveau took this ideal one step further by incorporating elements of the natural world into its designs, creating a style that was both innovative and elegant.
Art Nouveau was also characterized by its use of new materials and techniques, such as stained glass, enamel, and innovative printing processes. These new materials allowed designers to create intricate, highly detailed designs that were both visually stunning and technically advanced.
Some of the most famous examples of Art Nouveau architecture can be found in cities such as Paris, Brussels, and Barcelona, where buildings such as the Paris Metro entrances, the Horta Museum, and the Casa Batlló showcase the style’s emphasis on organic forms and decorative detail.
Art Deco: A Celebration of Modernity and Geometric Shapes
Art Deco, which emerged in the 1920s and 1930s, is a stark contrast to the organic forms and flowing lines of Art Nouveau. Instead, Art Deco is characterized by its geometric shapes, bold colors, and streamlined, modern aesthetic. The style was heavily influenced by the machine age, with designers drawing inspiration from the sleek, aerodynamic forms of automobiles, airplanes, and ocean liners.
Art Deco was also influenced by the rise of modernism in art and design, with designers such as Le Corbusier and Walter Gropius advocating for a more streamlined, functional approach to architecture and design. This emphasis on simplicity and efficiency can be seen in the clean lines and sharp angles of Art Deco buildings and furniture.
One of the key features of Art Deco is its use of exotic materials and luxurious finishes, such as chrome, glass, and polished wood. These materials conveyed a sense of glamour and sophistication, making Art Deco popular among the wealthy elite of the time.
Some of the most iconic examples of Art Deco architecture can be found in cities such as New York, Miami, and Los Angeles, where buildings such as the Chrysler Building, the Delano Hotel, and the Bullocks Wilshire showcase the style’s emphasis on modernity and luxury.
Contrasting Aesthetics: Art Deco vs. Art Nouveau
While both Art Deco and Art Nouveau are known for their intricate designs and emphasis on craftsmanship, there are several key differences that set the two styles apart.
Materials and Techniques
Art Nouveau designers favored organic materials such as wood, glass, and ceramic, as well as new techniques such as stained glass and enamel. These materials allowed for the creation of highly decorative, intricate designs that were reminiscent of the natural world.
Art Deco designers, on the other hand, favored modern materials such as chrome, glass, and polished wood, as well as streamlined, functional designs. These materials conveyed a sense of luxury and sophistication, making Art Deco popular among the wealthy elite of the time.
Forms and Motifs
Art Nouveau is known for its organic forms, intricate motifs, and flowing, curvilinear shapes. The style was heavily influenced by the natural world, with designs often incorporating elements such as flowers, leaves, and vines. One of the most distinctive features of Art Nouveau is the use of "whiplash" curves, which create a sense of movement and grace.
Art Deco, on the other hand, is characterized by its geometric shapes, bold colors, and streamlined, modern aesthetic. The style was heavily influenced by the machine age, with designers drawing inspiration from the sleek, aerodynamic forms of automobiles, airplanes, and ocean liners. Art Deco designs are characterized by clean lines, sharp angles, and a sense of symmetry and balance.
Color Palette
Art Nouveau designers favored a soft, muted color palette, with earth tones such as greens, browns, and yellows predominating. These colors were often used to create a sense of harmony and tranquility, reflecting the style’s emphasis on the natural world.
Art Deco designers, on the other hand, favored bold, vivid colors such as red, blue, and black, as well as metallic finishes such as chrome and gold. These colors were used to convey a sense of luxury and sophistication, making Art Deco popular among the wealthy elite of the time.
Influence and Legacy
Art Nouveau had a significant impact on the world of design, inspiring a generation of artists and designers to embrace nature and craftsmanship in their work. The style was highly influential in fields such as architecture, furniture design, and graphic design, with designers such as Hector Guimard, Louis Comfort Tiffany, and Alphonse Mucha creating iconic works that are still admired to this day.
Art Deco, on the other hand, had a more limited influence on the world of design, with the style falling out of favor in the years following World War II. However, Art Deco has experienced a revival in recent years, with designers and collectors alike rediscovering the elegance and sophistication of the style. Today, Art Deco is celebrated for its bold colors, geometric shapes, and modern aesthetic, making it a popular choice for those seeking a glamorous, retro-inspired look.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Art Deco and Art Nouveau are two prominent styles that emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Despite both being known for their intricate designs and emphasis on craftsmanship, they differ significantly in their aesthetics, influences, and impact on the world of art and design.
Art Nouveau is characterized by its organic forms, intricate motifs, and flowing, curvilinear shapes, with designs often incorporating elements such as flowers, leaves, and vines. The style was heavily influenced by the natural world and the Arts and Crafts movement, creating a look that was both innovative and elegant.
Art Deco, on the other hand, is characterized by its geometric shapes, bold colors, and streamlined, modern aesthetic, drawing inspiration from the sleek, aerodynamic forms of the machine age. The style was popular among the wealthy elite of the time, with designs featuring exotic materials and luxurious finishes that conveyed a sense of glamour and sophistication.
While both styles have left a lasting impact on the world of design, they each offer a unique aesthetic that continues to inspire artists and designers to this day. Whether you prefer the flowing, organic forms of Art Nouveau or the bold, geometric shapes of Art Deco, there is no denying the enduring appeal of these two influential styles.





Leave a Comment